Issue.11 - A Catalyst for Economy
Right in front of our eyes.
Feedback Mural

11. Introduction
Hey.
Today I bring up a serious topic.
In a serious and objective tone.
As we saw on “MetaNews.1 - March Digest”, Newsboy brought us an article about the climate crisis.
This edition, though, won’t be a lecture on why we need to be more conscious in regards to the planet Earth we are leaving behind for future generations.
A slide from the AR6 Synthesis Report attached in Metanews.1 already says it all: “Our choices will reverberate for hundreds, even thousands of years.”
From my experience, people tend to have two different perspectives on such a sentence:
a) “I don’t have time to think about healthy soil for food cultivation a hundred years from now. I need to do something that drives me profit now because I’m alive now and my business needs cash flow now because I need to pay my employees now otherwise I go bankrupt right now.”
b) “It is past time we take action. Consider myself enlisted for the battle.”
This article is mostly for As, but please stick around Bs.
Because by the end, everyone will be able to understand that saving the planet Earth will be the true source of profit for companies in most industries in the following years.
Not because without planet Earth there won’t be a place left to make a profit or… live, but simply because thinking sustainably and offsetting carbon will make your company not only survive what is to come but also profitable in many different ways.
I will make it my mission to prove that below.
The following might be puzzling, but understanding the dynamics behind carbon offsetting and the carbon market will be essential. Please bear with me, reader.
What we have today are industries, electronic devices, deforestation, livestock farming, transportation, waste management, and many other verticals feeding on electrical energy derived from fossil fuels that are made with hydrocarbon compounds, dangerously increasing the supply of carbon dioxide (CO²) in the atmosphere and driving climate to deteriorate by doing so.
Please refer to the attached diagram for a clearer picture. Download the PDF for full resolution.
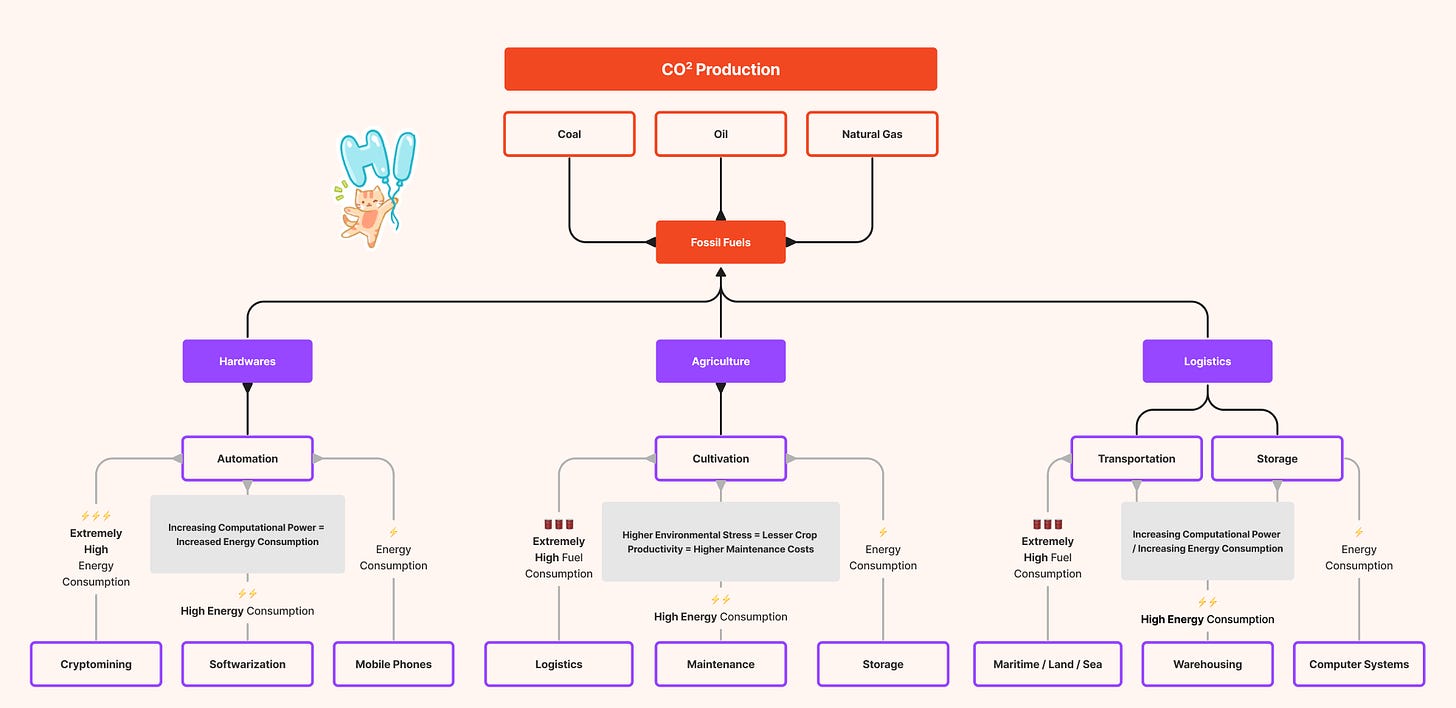
The burning of fossil fuels is a major source of human-induced CO2 emissions, which contribute to the greenhouse effect, global warming, and climate change.
But why do we have to burn fossil fuels? Because we need energy.
The car that you drove today needed fuel in order to function.
The computer you use to work needs electrical energy in order to function.
The plug you use to charge your phone is connected to a public electrical infrastructure that stores electrical energy in order to power cities.
The electrical energy, stored in these infrastructures, powering your house, your office, your local supermarket, your country’s industries, and your phone plug are generated by fossil fuels, which are a non-renewable source.
Globally, a rough estimate would be that 80-85% of all energy produced today comes from these non-renewable sources (fossil fuels).
Whereas, 15-20% comes from renewable sources, Solar energy, wind energy, hydropower, geothermal energy, biomass energy, tidal and wave energy.
So there is a harmful surplus of Carbon Dioxide (CO²) in the atmosphere and it is increasing while you read this.
Here’s the flip of the switch.
Economists say: “Supply creates its own demand”
But this doesn’t apply to this much-needed resource that we are talking about.
Why?
Because there isn’t a demand for more supply of Carbon Dioxide (CO²).
There isn’t a demand for more supply of Oxygen (O²) either.
Production of (CO²) doesn’t decrease the supply of (O²) in the atmosphere.
We don’t need more (O²) in the atmosphere, we just need less (CO²) in the atmosphere.
This essentially means that.
The true resource is “Removal of (CO²)”
The supply is “Removal of (CO²)”
And the demand is for “Removal of (CO²)”
Long story short:
The scarcity of a common supply/resource increases its value and demand.
Whereas the excess of (CO²) increases the value and demand for its removal.
The dynamic for this resource is inverted because we are producing more than we should and hurting the environment by doing so.
The resource “Removal of (CO²)”, is known by two distinct names “Carbon Offset” and “Carbon Removal”, these are related but distinct concepts but I won’t talk about that in this edition.
Both of them generate Carbon Credits, which can then be traded or sold for FIAT currencies to businesses, industries, governments, or even non-governmental organizations that need to offset their own emissions.
11.1 Resources
The valuable assets of human barter.
Now we need to understand why this resource we just discussed is so important at this moment. For that, let’s dive into the concept of “resource”
A resource is a term used to describe anything useful or valuable to individuals or organizations, because of that, they are used for trade (barter).
We can categorize all economical resources into two categories: material resources and intangible resources. Some examples are below.
Material resources:
Natural resources (e.g., oil, coal, minerals, water)
Agricultural resources (e.g., crops, livestock)
Human-made resources (e.g., buildings, machinery, infrastructure)
Energy resources (e.g., fossil fuels, renewable energy sources)
Financial resources (e.g., money, stocks, bonds)
Consumer goods (e.g., food, clothing, electronics)
Intangible resources:
Intellectual property (e.g., patents, trademarks, copyrights)
Human capital (e.g., skills, knowledge, experience)
Reputation and brand value
Organizational culture
Customer and supplier relationships
Information, data, and digital tools (e.g., software)
Legal rights and protections (e.g., contracts, licenses)
Now let’s hypothesize the main resources that nurtured economical growth in society throughout the last 10 decades:
1900s: Coal (Material Resource)
1910s: War production (Material Resources)
1920s: Automobiles (Material Resources)
1930s: Infrastructure projects (Material Resources)
1940s: War production (Material Resources)
1950s: Consumer goods (Material Resources)
1960s: Space Race (Material Resources)
1970s: Oil (Material Resources)
1980s: Finance (Material Resources)
1990s: Internet/Globalization (Intangible Resources)
2000s: E-commerce (Intangible Resources)
2010s: Software (Intangible Resources)
2020s: ?
I can only think of three potential labels to put on the current decade: 1) AI Technology; 2) Cryptocurrency and 3) Carbon Offset/Removal.
(Let’s just hope it is not “War Production” again.)
All of these resources have one thing in common.
They are intangible resources.
You can’t touch them with your hands.
But here’s the golden catch.
The first two increase the demand for the third.
I have to repeat that.
The first two increase the demand for the third.
Why?
A) Because AI Technology and Cryptocurrency feed on the electrical energy that is generated by the exact same thing that generates an excess of (CO²) in the atmosphere: hydrocarbon-derived fossil fuels.
B) Because of all these 3 resources, two of them are entirely digital and intangible but only one of them, although also intangible, is directly related to nature and can only be generated in… nature.
C) Technology feed on energy that feeds on nature which feeds on itself.
D) Technology depends on nature to exist and nature depends on a healthy atmosphere to function as it should.
E) Demand for “Carbon Offset/Carbon Removal” will drastically increase in the following years and it will be for some time the most valuable resource in the world.
F) The economical recession will cause more contraptions in the cash flow of governments from different countries, driving them to find a new source of income.
G) This new source of income for governments will be the taxation of carbon emissions. Countries will grow strongly by taxing the emission of their corporations and industries.
H) Demand for “Removal of (CO²)” will explode as companies all around the world will start purchasing Carbon Credits to offset their emissions and comply with regulations.
I) Companies that can’t offset their emissions will go bankrupt in a flood of taxes and regulatory fines.
J) Companies that offset their emissions will survive and grow their market share by filling the demand of companies that didn’t survive the eco-transition.
10.2 The Nature of an Intangible Asset
Is it real if it can’t be seen by our eyes?
If you want to offset carbon from the atmosphere, you should first understand the nature of this asset.
Because just like a crypto active (e.g. Bitcoin), “Removal of (CO²)” is not a piece of paper that you can touch with your hands.
They are both Data, a set of traceable information that validates the value of the resource.
Resources can be either deflationary or inflationary.
Deflationary resources tend to become scarcer because they become harder to find and tend to have a finite supply, their value is likely to increase due to their rarity. (Like land, gemstones, and precious metals)
Inflationary resources tend to become more abundant because they can be produced or replenished continuously, and their supply can grow over time, decreasing their value. As a result, their value is likely to decrease or remain stable due to their availability and the ease of producing more of them. (Like money, food, and manufactured goods.)
Let’s try to structure the framework behind a truly deflationary and intangible resource: Bitcoin.
Bitcoin validates itself as a resource in multiple ways:
A) SUPPLY/DEMAND: The decentralization aspect of Bitcoin generated value and demand. The deflationary nature of Bitcoin makes itself automatically decrease its supply and increase its demand. By 2140, all 21 million bitcoins will have been mined and they won’t be generated/mined anymore.
B) VALUE: Decentralized nature; Limited supply; Digital and borderless; Hedge against inflation and economic uncertainty (Like digital gold)
C) UTILITY: The different utilities behind the technology made it undeniable: Sole ownership; global reach; digital payments; security; transparency; financial inclusion; investments.
D) DISTRIBUTION: An ecosystem has been developed around it, and the supply/demand empowered the technology behind it, reaching new utilities. Cryptocurrency brokerage surged and connected FIAT currency to the ecosystem, making it possible to exchange and convert the asset with real money, in real-time.
Now let’s try to apply this model to the intangible resource we have been talking about: “Removal of (CO²)”
A) SUPPLY/DEMAND: Some people might disagree but the resource “Removal of (CO²)” has both an inflationary and deflationary nature. If global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions are successful, there may come a time when carbon offsetting is no longer necessary or the demand for it diminishes significantly. With this in mind, the growing excess can drive an incessant demand and in the context of the excess being neutralized, the demand will diminish. (It is important to note that there isn’t a need to remove all the CO² from the atmosphere because the atmosphere does need some CO² in its composition in order to function properly.)
B) VALUE: The increasing dangers of climate change are making the excess of Carbon Dioxide (CO²) in the atmosphere an immediate threat to the health of flora, fauna, and society. The demand for “Removal of (CO²)” comes from the need to mitigate the environmental consequences of this excess before we face more droughts, famine, and climate disasters.
C) UTILITY: The utility behind “Removal of (CO²)” is much broader than we can measure. It starts as a truly sustainable act to preserve the environment for future generations by reducing emissions but resonates in positive public opinion for brands; compliance with regulations; financial incentives and a sustainable corporate culture where employees find purpose in their work. (Wouldn’t you give your best for a company that is legitimately helping save planet Earth?)
D) DISTRIBUTION: As the demand increases, new regulatory infrastructures are being developed in order to validate, register, monitor, verify, and trade “Removal of (CO²)”. When it comes to trade, the purchase can come from different entities: Companies and industries; governments; non-governmental organizations (NGOs); educational institutions; event organizers, and individuals. Brokers are surging in order to intermediate these exchanges through processes that will become faster and more accessible by the day.
10.3 Generating “Removal of (CO²)”
Validate, register, monitor, verify, issue, trade, and retire.
This might be the most important chapter in this issue.
I will make quite a bold affirmation because I have thought very hard about this.
Every type of company can offset carbon and generate “Removal of (CO²)” by improving their supply chain with sustainable mechanisms (decarbonization) except technology companies.
Technology companies that build software can’t mitigate their emission of carbon in their supply chains.
Why?
Technology companies rely on electrical energy to create digital products and services. While the employees working in these companies are part of the natural world, the technology industry itself generally has limited direct interaction with nature, except when their software is designed for use in industries that engage with the natural environment.
So the only way for technology companies to mitigate their CO² emissions is mostly by purchasing carbon offset from other industries.
Hence, most of the carbon offset purchases in the carbon market shall come from the technology industry in the following years.
On a counterpoint, in all other types of industry, it is possible to generate “Removal of (CO²)” through the decarbonization mechanism and sustainable projects.
All you have to do is map out the sources of energy consumption in your supply chain, quantify them, and start developing sustainable alternatives that might be more expensive in the short-term, but that will generate “Removal of (CO²)” in the long-term, sometimes, even generating a surplus that can be sold in the carbon market.
Once you understand how much CO² your company is emitting, then all you have to do is measure how much your emission is decreasing within the new technologies and processes that you implemented. The resultant amount will be your supply of “Removal of (CO²)”.
On the other hand, if you are a company that is directly related to nature, like agriculture companies, then you are in a position to generate a lot of “Removal of (CO²)” and even turn it into a potential business model. Crops and plants grow by absorbing carbon from the atmosphere and storing them in the soil, this means that adopting sustainable methods of farming and measuring the data in your soil can make it possible for you to profit from something that you are already doing but that can’t be monetized or traded because even though the “Removal of (CO²)” is being generated, it is not being measured and can’t be validated nor sold.
Chords
This is a song from my favorite band as a teenager.
Noisy, huh?
There are a lot of words in these lyrics and most of their songs talk about the current state of society and the environment.
When it all comes down
Will you say you did
Everything you could?
When it all comes down
Can you say that you never gave up?
Or were you standing by
To watch it fall away?
At the end of the day, we all have an eco-terrorist within us, but the time has come to be more conscious of nature.
Simply because being conscious of nature is the same thing as being conscious of our organic origin.
And being truly conscious of our origins is what always drove us to be better for those who came before us and made everything possible.
Differ what are lies from what is truth.
You know it.
Differ what is real from what is synthetic.
You know it.
Realize that you, the earth, and others are plural.
Ubuntu.
This is an African indigenous philosophy.
“I am because we are.”
“I am because you are.”
Just keep the following in mind:
Technology is binary and synthetic. Your life is singular and organic.
About the Author
Thiago Patriota
Made in 1996. Born & Raised Brazillian. Bachelor’s Degree in Advertising and Communication. Adept to autodidactism. Curious Soul. Published Author. Founder of Sentient.
That’s me in a nutshell but you can learn more about Agency and myself on the About page!
Contact
+1 302 261 3824
thipatriota@gmail.com





